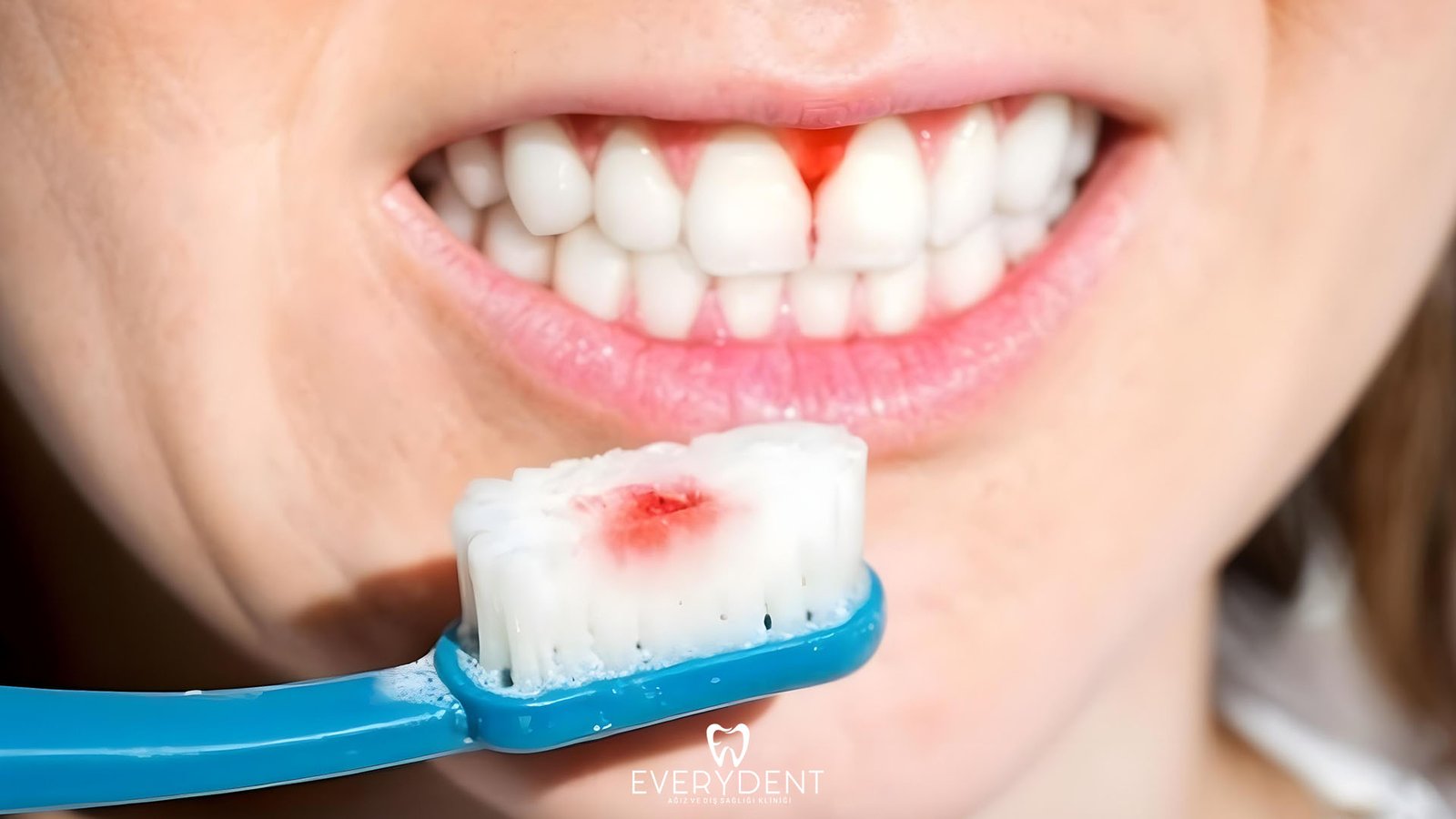
Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums is a common dental health problem that many people encounter in their daily lives, but are often ignored. This condition, which usually occurs during brushing or spontaneously, can be a sign of serious problems that can range from mild problems such as gingivitis to tooth loss. Bleeding gums is a condition that can affect not only oral and dental health, but also general health. For example, studies reveal that gum diseases may be associated with systemic conditions such as heart diseases and diabetes.
Although this problem mostly occurs due to gingivitis or periodontal diseases, it may also be due to different reasons such as vitamin deficiencies, hormonal changes, wrong tooth brushing techniques or smoking. Although it may seem like a minor problem at first, if left untreated over time, it can lead to gum recession, bone loss and even tooth loss. Therefore, understanding the causes of bleeding gums, recognizing its symptoms and learning the correct treatment methods are the first step to having healthy gums.
Why Do Gums Bleed?
Bleeding gums is a common health problem that can occur due to different reasons. This condition can often manifest itself as neglected oral hygiene or as a symptom of other underlying health problems. A proper understanding of the factors that cause bleeding gums is critical to preventing and treating this problem. We have listed the most common causes of bleeding gums below:
Gum Inflammation (Gingivitis)
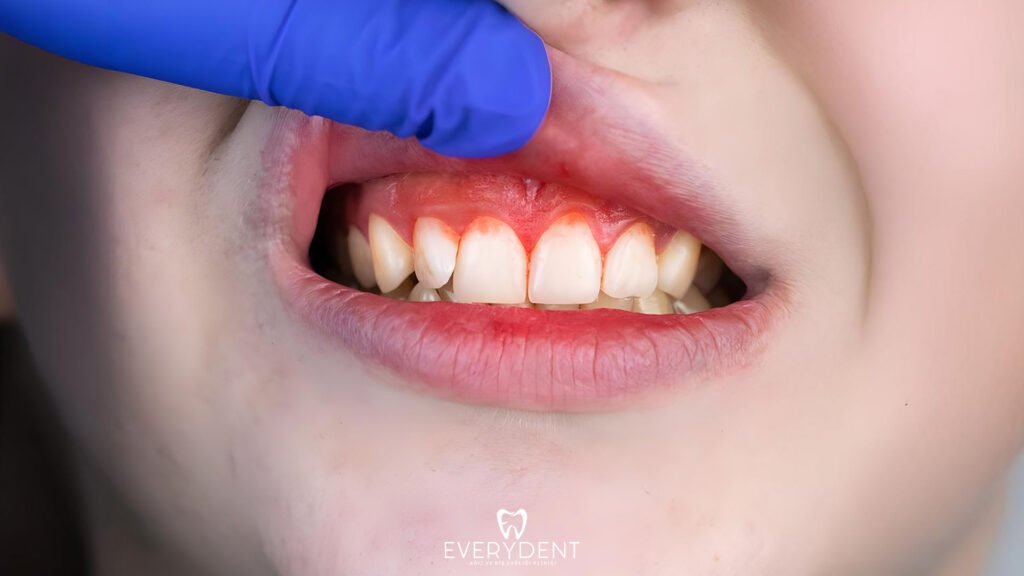
Gingivitis, one of the most common causes of bleeding gums, occurs when oral hygiene is not paid enough attention. Plaque accumulates on the surface of the teeth and at the gum line, creating an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to multiply. These bacteria cause inflammation in the gums, causing the gums to become red, swollen and tender.
Early symptoms of gingivitis include bleeding gums, bad breath, and tender gums. This bleeding, which is usually noticed during brushing or flossing, may indicate that the condition is progressing. Gingivitis can be treated early with correct oral care habits. However, if neglected, it can turn into more serious gum diseases.
Periodontitis (Advanced Gum Disease)
If gingivitis is not treated in time, it can turn into a more serious gum disease called periodontitis. Periodontitis is a disease that affects not only the gums but also the bone tissue that supports the teeth. In this case, the gums separate from the teeth, causing spaces called pockets to form. These pockets become a home for bacteria and allow the infection to spread deeper.
Bleeding gums during periodontitis are quite common and can lead to serious problems, including tooth loss, in the advanced stages of the disease. This condition may also manifest itself with symptoms such as bad breath, loose teeth and receding gums. In the treatment of periodontitis, professional teeth cleaning, inflammation control and, if necessary, surgical interventions may be required.
Improper Brushing and Flossing
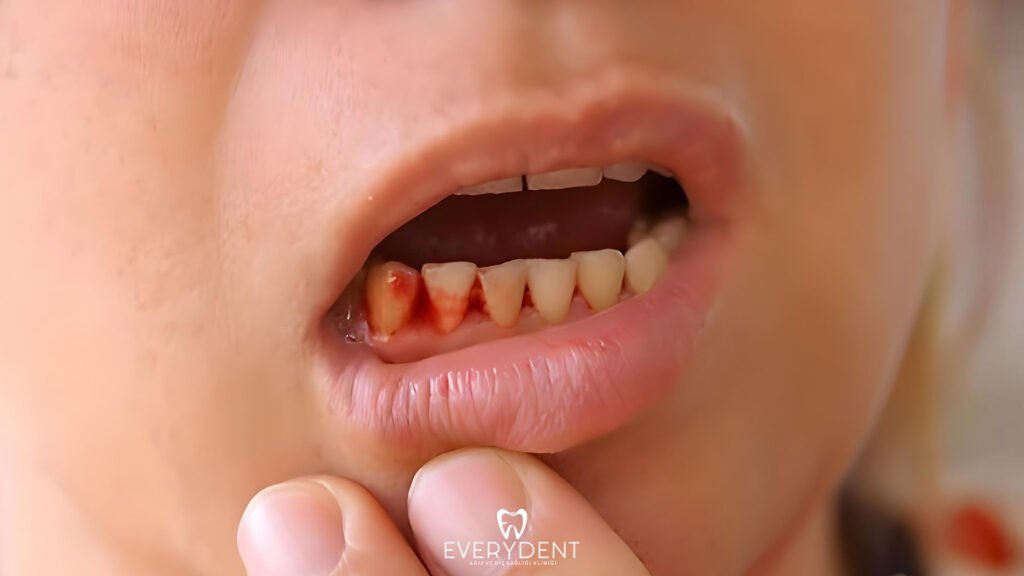
Another common cause of bleeding gums is brushing the teeth with incorrect techniques or using dental floss incorrectly. Brushing your teeth too hard can cause unnecessary irritation and damage to your gums. Especially when hard-bristled toothbrushes are used, micro injuries may occur on the gums and these injuries may lead to bleeding over time.
Similarly, uncontrolled use of dental floss can also damage the gums. Passing the floss quickly and hard between the teeth can sharply traumatize the gum tissue. This situation paves the way for the gums to become sensitive and bleed. Learning correct brushing techniques and choosing soft-bristled toothbrushes is important to protect gum health.
Vitamin Deficiencies
Lack of certain vitamins in the body can cause problems such as bleeding gums. Especially vitamin C and vitamin K deficiency can cause weakening of gum tissue and increased bleeding tendency.
Vitamin C plays an important role in keeping the immune system strong and regenerating tissues. In case of deficiency, gums become vulnerable and bleeding may occur even in minor trauma. Vitamin K has a critical role in blood clotting. Deficiency of this vitamin can easily lead to bleeding not only in the gums but also in other parts of the body.
What Causes Bleeding Gums During Pregnancy?
Many hormonal changes occur in women’s bodies during pregnancy. These hormonal changes can also affect the gums, causing gum bleeding. Increased estrogen and progesterone levels, especially during pregnancy, can cause gums to become more sensitive and increase the risk of inflammation.
This condition, which occurs during pregnancy, is often called “pregnancy gingivitis”. This condition, which manifests itself with swelling, redness and bleeding in the gums, can be worsened by neglecting oral care. Additionally, due to hormonal changes, gums become more vulnerable to bacteria, increasing the risk of inflammation.
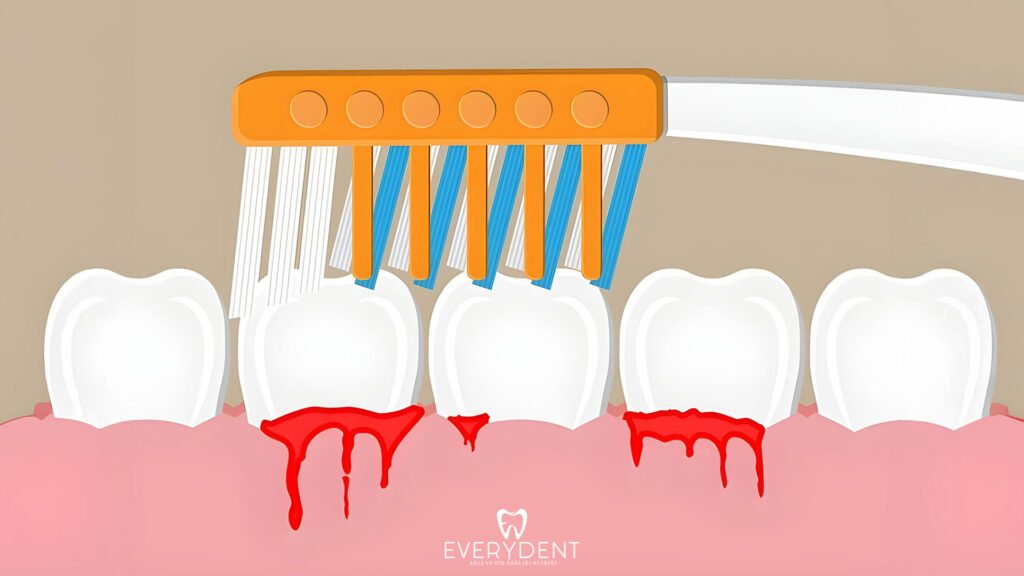
Bleeding Gums Treatment
he first step to treating and preventing bleeding gums is to establish a regular and proper oral care routine. Teeth should be brushed with a soft-bristled toothbrush with the correct technique at least twice a day, and the interface should be cleaned using dental floss. In addition, the dentist should be visited regularly to have professional teeth cleaning done and the accumulation of tartar and plaque should be prevented. A balanced diet is also of great importance for healthy gums; Consumption of fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins C and K can strengthen gums and reduce the risk of bleeding.
Additionally, quitting or minimizing habits that negatively affect gum health, such as smoking and alcohol, can help prevent bleeding. If the cause of gum bleeding is a disease such as gingivitis or periodontitis, the progression of the problem can be stopped by your dentist by applying appropriate treatment methods, such as root planing, surgical procedures or drug therapy. These precautions and regular physician checks are the basic steps for healthy gums.