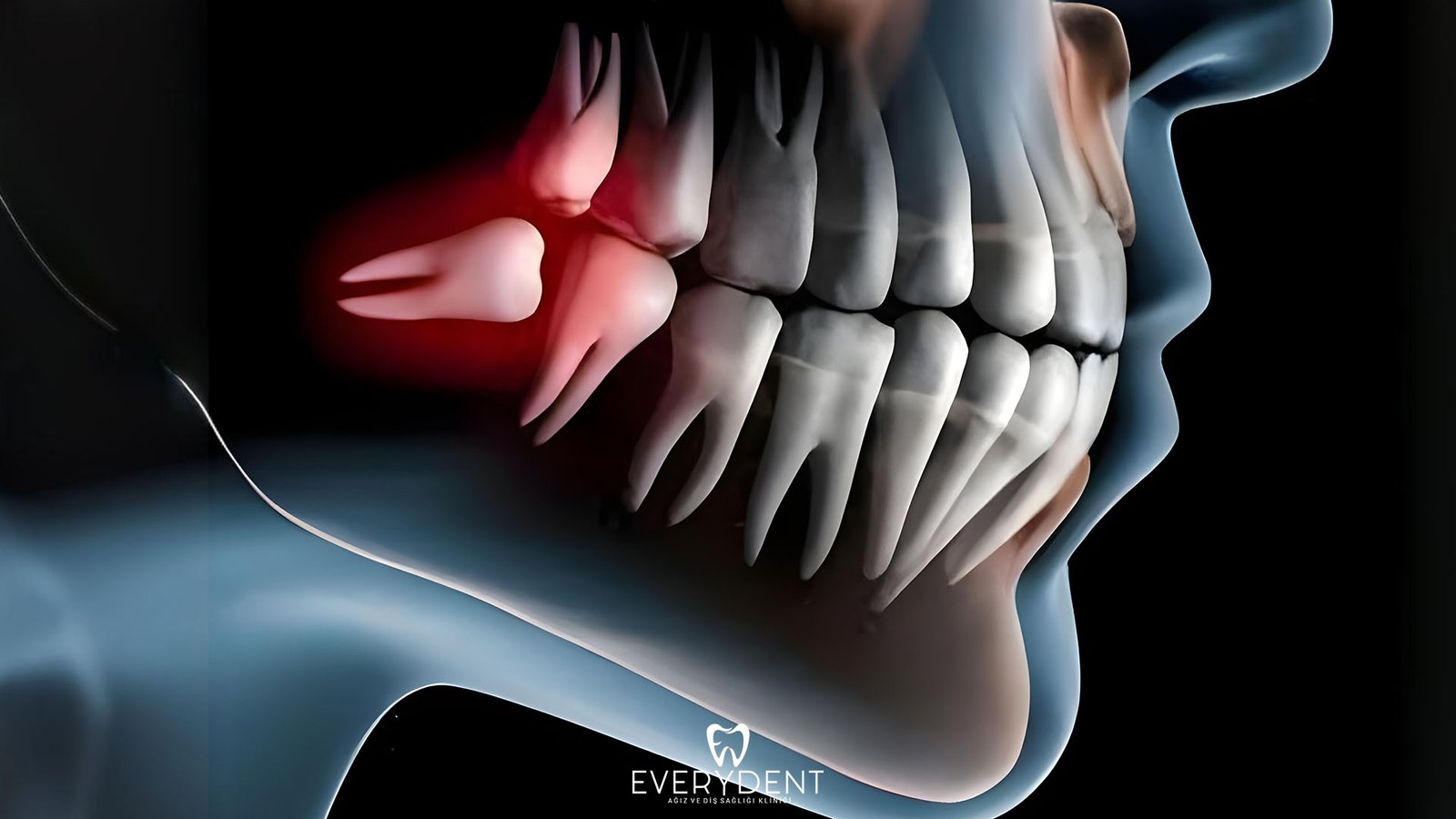
Impacted Tooth Extraction
In some cases, teeth cannot grow in accordance with the mouth structure and may remain impacted. Impacted teeth usually get stuck in the jawbone or cannot complete their development under the gums. This situation not only causes aesthetic concerns, but can also lead to serious health problems. Impacted teeth, which cause complications such as jaw pain, swelling, infection, damage to adjacent teeth, and even tooth loss, often require surgical intervention.
Here, we will discuss with you why impacted teeth occur, how to detect them and what treatment methods can be applied. Let’s take a closer look at this important issue to protect your health and smile. First of all, our first topic is what and why an impacted tooth is…
What is an Impacted Tooth?
Impacted teeth are teeth that should be in the mouth but cannot reach their natural position and remain under the jawbone or gums. Most often, this is caused by reasons such as not having enough space for the tooth to emerge, narrowness in the jaw structure, or the tooth developing in an incorrect position. Although impacted teeth are common, especially in wisdom teeth, similar situations may be encountered in other teeth. This situation affects both the oral structure and the surrounding tissues, causing various health problems and pain.
Impacted teeth are generally not easily noticed in the early stages and do not cause significant discomfort or pain. However, over time, it can put pressure on surrounding tissues, causing pain, swelling and inflammation. In particular, a tooth stuck in the jawbone can squeeze neighboring teeth, disrupting their arches and causing problems in tooth alignment. Additionally, there may be a risk of infection in the area where the impacted tooth is located, and this infection may threaten your entire oral health over time.
Another important effect of impacted teeth is that they can lead to jaw cysts or tumor-like formations. This condition may cause weakening of the jawbone and complications that require serious surgical interventions in the future. In addition, bacteria formed around impacted teeth can cause gum diseases and bad breath.
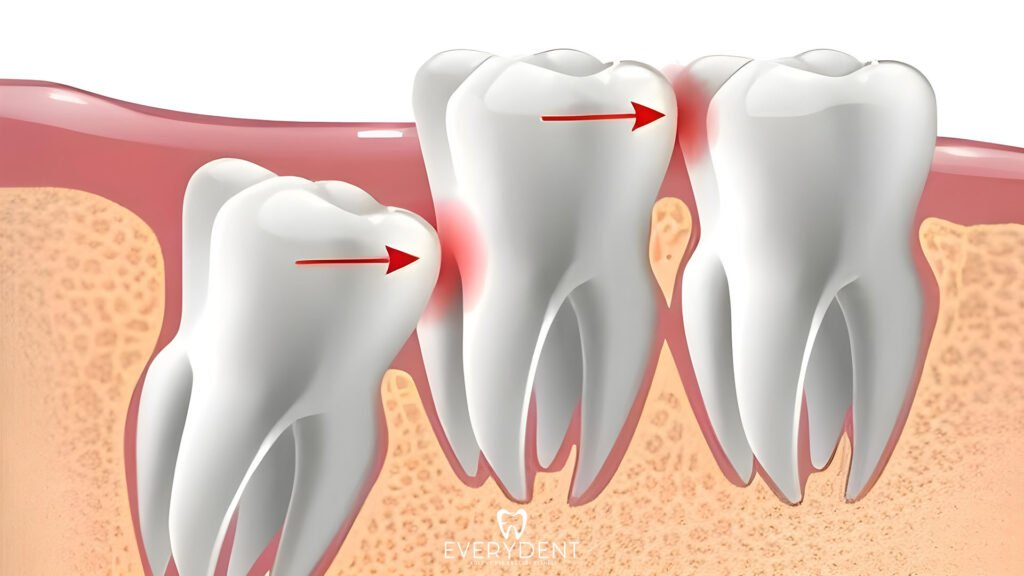
Why Impacted Teeth Cannot Come Out
There are a few basic factors why the impacted tooth cannot move to its normal position;
- Narrowness in the Jaw Structure: When there is not enough space for the teeth to emerge, the risk of impaction increases. This situation is common, especially since wisdom teeth appear after the development of the jaw bones is completed.
- Wrong Position: Abnormalities in the angle of emergence of the teeth may cause them to lean against other teeth and remain impacted.
- Genetic Factors: This condition is more likely to occur in individuals with a family history of impacted teeth.
- Orthodontic Problems: Alignment problems in the jaw and tooth structure can cause teeth to remain impacted.
Symptoms of Impacted Teeth
Although impacted teeth do not always cause obvious symptoms, they often manifest themselves with various discomforts. These are the situations we encounter most frequently:
- Constant or Intermittent Pain
When an impacted tooth puts pressure on the surrounding tissues, it causes constant pain or sudden pain during chewing. This pain is usually felt deep in the jawbone or gum and can worsen over time.
- Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling, redness and sensitivity may occur as a result of inflammation in the area where the tooth is trying to emerge. If the infection progresses, this swelling may spread to a larger area in the mouth and increase the feeling of discomfort.
- Restriction in Jaw Movements
Impacted teeth, especially in the lower jaw, can cause difficulties in jaw movements. A feeling of tension may be experienced when opening or closing the jaw, which can negatively affect daily activities, especially eating or speaking.
- Pressure and Crookedness in Adjacent Teeth
The impacted tooth can put pressure on other nearby teeth, disrupting their alignment. This may cause the teeth to become crooked or the closing pattern of the mouth to change.
- Cyst and Similar Formations
Untreated impacted teeth may cause fluid-filled cysts to form around them. These cysts can grow over time, weakening the jawbone and causing serious complications if left untreated. In rare cases, tumor-like structures may develop and more extensive surgical interventions may be required.
It will be more advantageous for both the physician and the patient if intervention is made earlier, as a result of regular dental check-ups, without waiting for the discomfort caused by these symptoms.
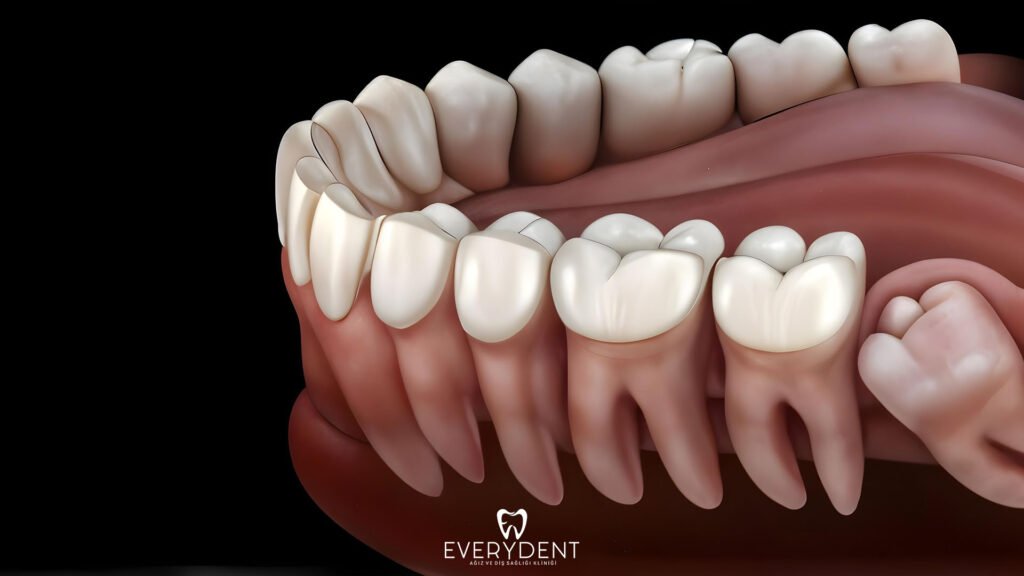
Why Should Impacted Teeth Be Extracted?
Impacted teeth that are left untreated can threaten not only the area where they are located, but the entire oral health. Failure to intervene in these teeth in a timely manner may cause serious problems both aesthetically and functionally. Impacted teeth may need to be extracted if there is one or more of the following reasons:
May Damage Neighboring Teeth
Impacted teeth can put pressure on the surrounding teeth and damage their roots. This pressure may cause decay, loosening, or deformation of the roots of adjacent teeth. Additionally, it may cause permanent problems in the oral structure by disrupting the position of healthy teeth.
Infection and Gum Problems
The tissues around the impacted tooth may become infected. Although these infections may initially present as mild pain and swelling, if left untreated, they can turn into gum abscesses or more widespread infections. In some cases, these infections even pose a risk of spreading to other parts of the body.
Disorders in Jaw and Teeth Structure
The pressure exerted by impacted teeth as they try to emerge can disrupt the natural alignment of the teeth. This causes crowding and jaw closing problems. Especially in people who have received orthodontic treatment, this irregularity caused by impacted teeth may negatively affect the results of previous treatment.
Cyst and More Serious Complications
Fluid-filled cysts may form around impacted teeth. These cysts can grow over time, damaging the jawbone and leading to tooth loss. If left untreated, it can weaken the structure of the jawbone and require more complex surgical interventions.
How is Impacted Tooth Extraction Done?
Impacted tooth extraction is a procedure usually performed by a dentist or oral and maxillofacial surgeon. The procedure is performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and the position of the tooth.
- Examination and Planning: Before the procedure, x-ray or tomography is taken to evaluate the position of the tooth and its effect on the surrounding tissues.
- Anesthesia: The patient is prepared with a suitable anesthesia method so that he does not feel pain during the procedure.
- Tooth Extraction: The tooth is accessed by making a surgical incision depending on the position of the tooth. If the entire tooth cannot be extracted, it is removed in pieces.
- Stitching and Care: After the procedure, the gum is stitched and care instructions are given to the patient.
Post-Extraction Recovery Process
The healing process after impacted tooth extraction may vary from patient to patient. However, general points to consider are:
- First 24 Hours: Ice packs can be applied to control bleeding and reduce swelling.
- Pain Management: Painkillers and antibiotics prescribed by the doctor should be used.
- Nutrition: Soft and warm foods should be consumed for a few days after the procedure.
- Oral Hygiene: The mouth should be cleaned carefully to prevent damage to the stitches.
Can Every Impacted Tooth Be Extracted?
Not every impacted tooth may need to be extracted; This depends on the location of the tooth, its effect on surrounding tissues, and the patient’s general oral health. If the impacted tooth does not cause any problems such as pain, swelling, infection or damage to neighboring teeth, regular follow-up is usually sufficient.
However, if an infection has developed around the tooth, if it puts pressure on neighboring teeth, if it causes cyst formation, or if there is a risk of damaging the jaw structure of the tooth, surgical intervention may be required. In such cases, your dentist will determine the most appropriate treatment plan for you.